
Solving the pulse problem
Cristina Esteban (ITAINNOVA), 21/11/2017
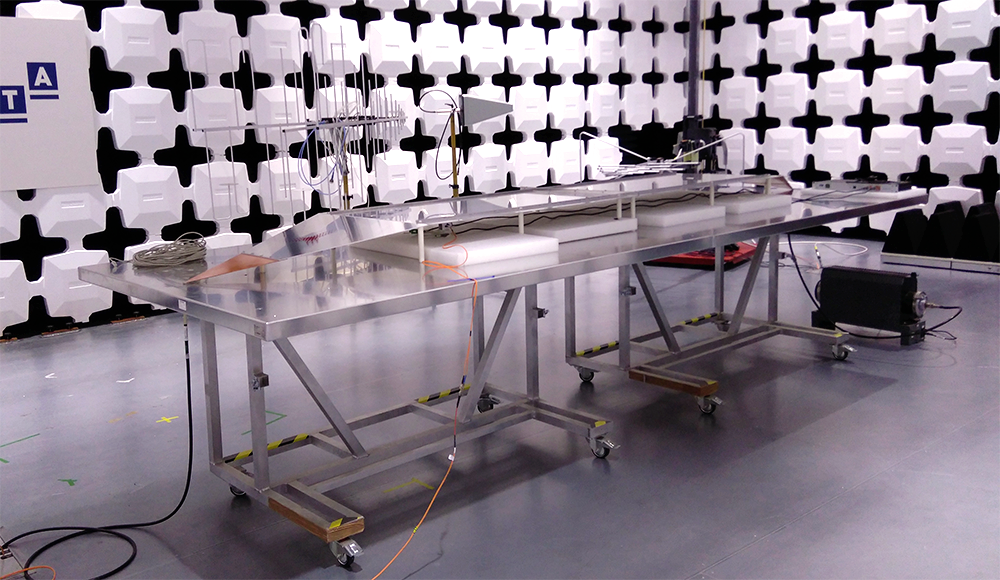
Stripline and DOSFET-Lo2 System during the susceptibility test at ITAINNOVA EMC Lab (Image: C. Esteban)
During summer 2017, researchers from Elettra Sincrotron Trieste in Italy were able to carry out testing at the electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) lab at ITAINNOVA in Spain. The test campaign was performed on DOSFET-Lo2, an advanced dosimetry system, as part of the Transnational Access programme of the AIDA-2020 project, which offers support for researchers to access ten European detector testing facilities.
The DOSFET-L02 system, developed in the context of the FERMI@Elettra Project, offers real-time monitoring of radiation dosage and allows users to take measurements in remote and inaccessible locations. For that purpose, performing an EMC characterization of the DOSFET system was important in order to ensure its correct performance in locations with different electromagnetic environments.
In the future, DOSFET systems may be used at pulsed laser facilities. Electromagnetic Pulse (EMP), a known issue for short-pulse laser facilities, causes electromagnetic interference in any electronics system in proximity. A significant source of EMP in these systems is thought to be due to the electrons which escape when the laser hits its target. This generates a wide-band, high power, interference pulse extending from the very low frequency (VLF) band to the very high frequency (VHF) band, with an energy range of 10-100 MHz.
As such, the DOSFET system needed to be characterized in the presence of high electric fields at a high frequency. For that purpose, researchers from ITAINNOVA designed a new EMC test with specific set-up parameters.
Indeed, the ITAINNOVA researchers developed a test set-up based on strip-lines and RF amplifiers, which was able to create strong electromagnetic fields from 10 kHz to 1 GHz and with an amplitude up to 1,4 kV/m.
This new test scenario allowed the Elettra team to obtain useful information, providing them the tools needed to predict the response of the DOSFET system in different pulsed laser areas. The ability to predict the behavior of the system is crucial in mitigating potential problems in the future caused by EMPs.
The test campaign carried out at ITAINNOVA is the first time that this type of characterization has been performed in a radiation sensor.
